Formulation and Evaluation of Fast Dissolving Oral Film of Lisinopril
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.62896/ijpdd.2.7.02Keywords:
Lisinopril, Fast-dissolving oral films, Drug delivery, Disintegration time, Tensile strength, In-vitro drug release, Stability study, Polymers, Solvent-casting method, Antihypertensive drugAbstract
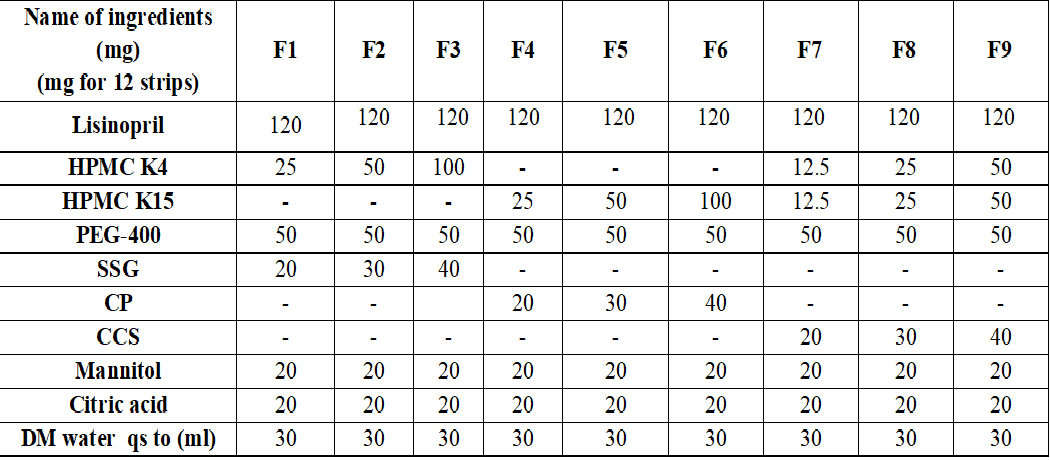
The present study focuses on the formulation and evaluation of fast-dissolving oral films of Lisinopril, an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor used for the management of hypertension. Fast-dissolving films offer several advantages over conventional oral dosage forms, such as ease of administration, enhanced patient compliance, and rapid drug release. Various formulation strategies were employed, including the use of different polymers and excipients to optimize the film's mechanical properties, disintegration time, drug release profile, and stability. The films were prepared using a solvent-casting method and evaluated for appearance, thickness, weight, folding endurance, tensile strength, disintegration time, moisture content, and assay. Formulation F7 showed the best performance, with a rapid disintegration time of 32 seconds, excellent mechanical properties, and a high cumulative drug release (98.89%) at 10 minutes. The in-vitro drug release profile of F7 followed the Peppas model with a non-Fickian diffusion mechanism. Stability studies indicated minimal changes in drug content over a 3-month period, confirming the stability of the optimized formulation. These findings suggest that F7 could serve as a promising fast-dissolving oral film for the delivery of lisinopril, offering a patient-friendly and efficient alternative to conventional tablets.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Sujata Publications

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.















